(Supported by the NSFC)
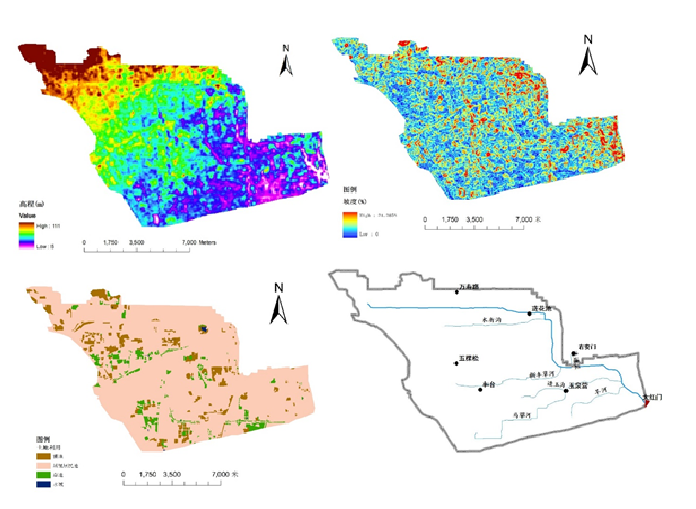
The project is under the auspices of Beijing Normal University and is being implemented in collaboration with the Beijing Municipal Institute of City Planning and Design. A distributed hydrological model, developed on the basis of the characteristics of the urban underlying surface, was developed for the Liangshui River basin in Beijing City. In light of a quantitative description of the underlying surface characteristics and a spatial superposition analysis of the confluence channels (e.g., rivers and streets), a grid distribution will be generated, reflecting the characteristics of the urban underlying surface flow routing. A previous study of runoff generation mechanisms led to the formulation of one- and two-dimensional hydrodynamic models that were used to simulate various patterns of flow routing in urban areas. The finite volume method will be used to establish the solution scheme. The model can better reflect the boundary characteristics of the flood evolution process and improve the efficiency and precision of the simulation of the urban flooding process through the use of multiscalar information mining to study the underlying surface.